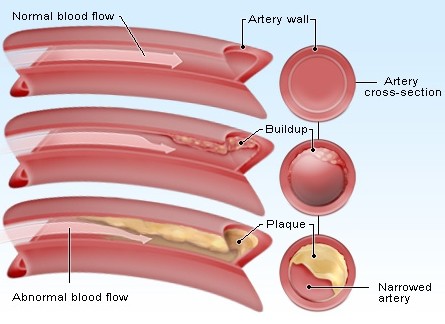
Arteries are blood vessels responsible for carrying blood that are rich in oxygen all over the body – from the inner recesses of the head till the tips of the toes. Obviously, their role to the human body is very essential. Unfortunately, some develop the condition of clogged arteries or arterial plaque which can cause for serious problems such as stroke, heart attack and even death. The arteries can be clogged by plaque buildup on its inner walls and this reduces the blood flow in the body and in some instances, it can block the flow entirely.
To prevent this from happening, it is of great importance that everyone knows what causes this condition and how to properly prevent or treat to avoid more serious complications in the end.
Causes of Clogged Arteries
There are many substances and properties that can circulate with the blood, including cholesterol, calcium, fat, fibrin and cellular waste. When these substances accumulate on the inner walls of the arteries, they turn into plaque buildup. More than this plaque buildup, the cells in the artery walls also have some secretions to make of their own and this can worsen the condition. The growth in plaque is called atherosclerosis and these causes for the arteries to become hard and narrow. Unfortunately, medical and health experts cannot guarantee how this condition starts; all they can vie for is the fact that this whole condition is a result of the damages done to the arterial wall.
Experts believe that the following factors can be the reason for having clogged arteries:
1. High LDL and Low HDL
HDL stands for High-Density Lipoprotein which is also known as “good cholesterol” while LDL stands for Low-Density Lipoprotein or sometimes referred to as “bad cholesterol”. HDL’s main function is to carry the cholesterol directly to the liver where it will be processed accordingly and will be released from the body. Because it is a stable molecule, it does not pose any danger to the arteries. LDL, however, is the one responsible for carrying cholesterol to cells all throughout the body. These cholesterols once carried out to the cells will then be used for different kinds of bodily functions. The thing with LDL is that this molecule oxidizes easily and tends to stick to the artery walls with ease.
The whole concept behind this risk factor is that we should have higher HDL but lower LDL in the body. This is because having low HDL poses a great risk to having clogged arteries simply because it is the molecule responsible for bringing LDLs directly to the liver and not have it adhere to the artery walls.
Here is a video about how cholesterol clogs the arteries:
2. High Blood Pressure
Another risk factor for clogged arteries is having a high blood pressure. When you have high blood pressure, there is a greater chance in speeding up the process of arterial plaque buildup. This also expedites the hardening of the clogged arteries.
3. Smoking Cigarettes
Aside from damages that it can do to the lungs, smoking cigarettes can also contribute to the clogging of the arteries.
Dangers of Clogged Arteries
The prevention of arterial plaque buildup should be taken seriously because this condition poses great dangers to someone’s life. It can not only lead to more serious complications but it can also cause death especially for cases that have been left untreated. Here are a few examples of the dangers that clogged arteries can pose to one’s health:
- Coronary Artery Disease. This condition is the most common cause for death in the United States. This happens when plaque gets piled up in the arteries that carry blood to the heart and then gets damaged or diseased.
- Carotid Artery Disease. The carotid arteries run in the sides of the neck, when arterial plaque gets piled up in these vessels and when not treated immediately and properly, can cause stroke.
- Peripheral Artery Disease. This kind of condition affects the legs and the feet. When plaque builds up in these vessels that carry blood to the legs, it can cause for serious infections including numbness and pain.
Symptoms for Clogged Arteries
Knowing about clogged arteries can cause for anyone to be concerned and afraid of his or her health. A lot of people ask if there are any symptoms to this disease in order to know when it is best to get immediate medical attention. Unfortunately, a lot of people have been victimized by this condition without any single sign until a major life threatening event takes place.
Health experts advise, however, that there are signs that can be considered as symptoms for this condition. This includes:
- Chest pain
- Shortness of breath
- Experiencing heart palpitations
- Feeling weak and dizzy
- Constant nausea
- Sweating without proper reason
It is advised that when feeling any of these symptoms in a constant basis, that the person should immediately seek medical attention.
Treatments for Clogged Arteries
The good thing about this condition is that it may be prevented and treated by a healthcare professional. To support prevention, one may go to the doctor and ask for an exam. According to its severity, the doctor may advise one or two of these solutions:
1. Lifestyle Changes
Living a healthy lifestyle is important to ensure that the arteries remain healthy and this can be done by having a balanced diet that is low in saturated fats and cholesterol and maintain a good intake of fresh fruits and vegetables. Maintaining a healthy weight is also important in keeping the arteries healthy as well as exercising regularly. And just as it would benefit one’s overall health, quitting smoking can contribute a great deal in having a healthy lifestyle.
2. Medications
You may be prescribed some medications in order to lower the cholesterol in the body, lower the blood pressure, and to thin the blood. These medications may greatly help in controlling the factors contribute to clogged arteries.
3. Surgical Procedures
When already suffering from this condition, there are a few surgical solutions that will have to be done in order to treat it. This includes stent placement, bypass surgery, and balloon angioplasty.